Life Skills and Developmental Competencies: What Are They and Why Are They Important
go.ncsu.edu/readext?575414
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲Every day there are media posts, news articles and public announcements commenting on the “skills- both life and soft” necessary for young people to acquire and utilize in order to transition successfully to adulthood. In today’s world, organizations, colleges, and employers are all prioritizing prospective applicants that demonstrate a capability in life skills instead of purely academic achievement. So what are these skills and how can you help your child acquire and master these important tools and competencies?
Life skills are important learned abilities and competencies that are essential for individuals, both young and old, to meet the challenges of everyday life. They are the building blocks that allow youth to apply the knowledge they acquire from formal and informal educational activities and experiences, and they are associated with managing and living a better quality of life and helping individuals accomplish their ambitions and living life to the fullest. It is important to note that the relevance of specific life skills is dependent on life circumstances, culture, age, and geography. For example, learning to drive and attaining a driver’s license are skills that would be of greater importance to a teenager in living in Currituck than they would be to a teenager living in New York City.
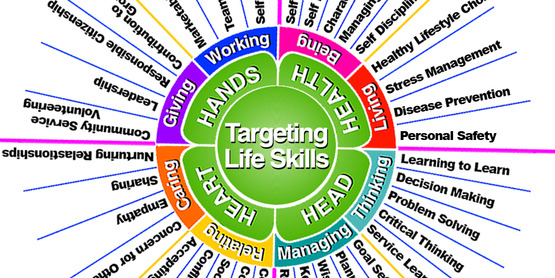
Hendricks, P. (1998) “Developing Youth Curriculum Using the Targeting Life Skills Model”
The development of healthy and productive life skills is the key component of 4-H youth development programming and we use a framework based on the 4-H Pledge (Head, Heart, Hands & Health), to organize and deliver educational experiences and activities that promote and support the development of these skills in youth. The “Targeting Life Skills Model for 4-H” (P. Hendricks, Iowa State University Extension, 1998), provides a system for connecting 4-H programs, projects and activities to both life skills and developmental competencies. This model identifies a list of specific skills that when learned, practiced and used by young people, lead to a capability and mastery of youth competencies that permit youth to effectively deal with the demands and challenges of everyday life. The 4-H focus on identified youth competencies are:
- Knowledge, Reasoning, and Creativity (HEAD) which addresses “Thinking” and “Managing” life skills such as decision making, problem solving and goal setting.
- Personal and Social (HEART) which addresses “Relating” and “Caring” skills such as effective communications, empathy, and cooperation.
- Vocational and Citizenship (HAND) which addresses “Giving” and “Working” skills like leadership, teamwork, and self-motivation.
- Health and Physical (HEALTH) which address “Living” and “Being” life skills such as healthy lifestyle choices, self-esteem, and responsibility.
There is a clear relationship between life skill acquisition and quality of life. Programs and activities offered through 4-H provide youth with the means to continuously expand and master skills necessary to become competent, caring, and competitive citizens in their community and world. Each month this year, Currituck 4-H will focus on a different life skill/competency in our educational articles and highlight available programs that provide youth opportunities that promote skill development. It is our purpose to partner with families and grow the next generation of leaders for our community.
For more information on 4-H youth programs and activities contact Sherry Fischlschweiger via phone, 252-232-2262, or email, sherry_fischlschweiger@ncsu.edu.
4-H is North Carolina’s largest youth development organization, equipping more than 263,000 young people each year with the skills to succeed and improve the world around them. 4-H programs and camps encourage young people to “learn by doing,” helping them to develop into active, contributing citizens. NC State Extension and the Cooperative Extension Program at N.C. A&T State University coordinate 4-H programs statewide.




